
Testosterone is associated with various male characteristics such as muscle mass, exercise performance, thick healthy beards, and is generally important for men's health.
Unfortunately as we age testosterone declines. Other factors such as stress, endocrine disruptors and an assortment of environmental toxins further contribute to low levels of testosterone.
Low testosterone is synonymous with decreased muscle mass and libido, along with an increase in body fat.
This article discusses evidence-based methods that can be used to effectively increase testosterone naturally and quickly, including, how to optimise free testosterone.
It also addresses frequently asked questions such as:
- Which foods increase testosterone the most?
- Which foods kill testosterone?
- Which foods lower estrogen the most?
- Does masturbating reduce testosterone?
So if you suffer from low testosterone, then this article is for you. By the end of it you will have gained a wealth of understanding with regard to how to harness the power of your HPTA.
The best part, regardless of your age, even if you are an older man (over 50 years old), these tips will still work.
Furthermore, you will also learn how to fast track your testosterone levels using highly efficacious natural testosterone boosting minerals.
Test-FX® T-Boosters™ For Men 150 Caps (12 NATURAL INGREDIENTS)

£44.99
£49.99
Test-FX® V 2.0: The Science-Based Testosterone Support Solution Test-FX Version 2.0, our potent new T-Support, isn't just a supplement; it's a evidence-driven nutritional marvel designed to effectively support healthy testosterone levels in the blood, for a flourishing, and vibrant life.… Read More
Testosterone: what separates the men from the boys
At the very core of every man, lies a magic molecule; testosterone. Testosterone is the primary male sex hormone and as such is what literally separates the men from the boys. Once a boy reaches puberty, his natural testosterone levels soar, and thus the boy makes the transition into the man.
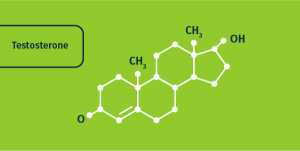
Testosterone has an empirical formula of C19H28O2, is produced in the testes and is largely responsible for the distinctive physical and behavioural differences between men and women.
Typically testosterone levels will peak in men between the ages of 20-28, slowly declining from the age of 30 onwards. Low testosterone levels are also associated with ageing, conversely; maintaining optimal testosterone levels has been shown to slow down the ageing process.
Testosterone regulation and hypothalamic pituitary testicular axis
The HPTA forms the relationship between the Hypothalamus, Pituitary and Testes. The HPTA connects all three individual endocrine glands in an intricate hormonal feedback mechanism unifying individual functions of all three glands into a singular system.
Here is a brief overview of the mechanism behind endogenous production of testosterone via the HPTA:
- Hypothalamus releases Gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH)
- GnRH stimulates the Pituitary gland to produce luteinising hormone (LH) & follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH)
- LH stimulates the Leydig cells of gonads to produce testosterone.
Testosterone replacement therapy (TRT)
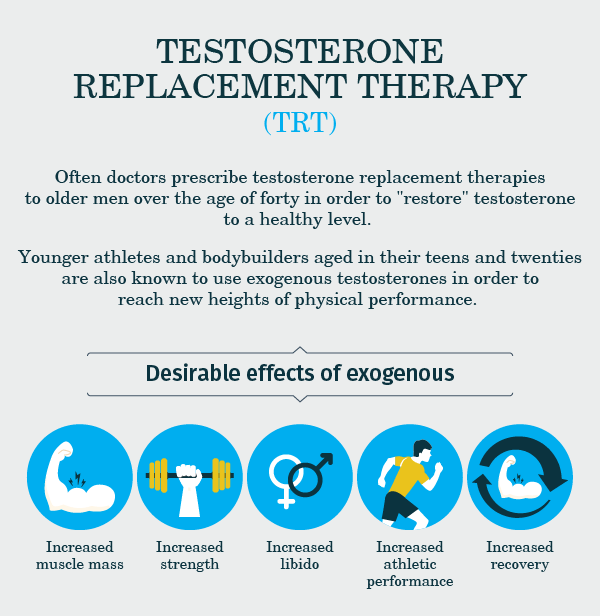
Often doctors prescribe testosterone replacement therapies to older men over the age of forty in order to "restore" testosterone to a healthy level.
Younger athletes and bodybuilders aged in their teens and twenties are also known to use exogenous testosterones and other such androgenic hormones in order to surpass levels of natural hormone production and thus reach new heights of physical performance.
Using a synthetic testosterone preparation is a sure fire way to increase testosterone levels and deliver all of its desirable effects, such as but not limited to:
- Increased muscle mass.
- Increased strength.
- Increased libido.
- Increased athletic performance.
- Increased recovery.
However these desirable effects of exogenous testosterone can only be maintained with its continued use. Cease its use and testosterone levels soon falter along with all of its associated benefits, followed by a catalogue of unwanted side effects.
The shocking truth about TRT (exogenous testosterone)
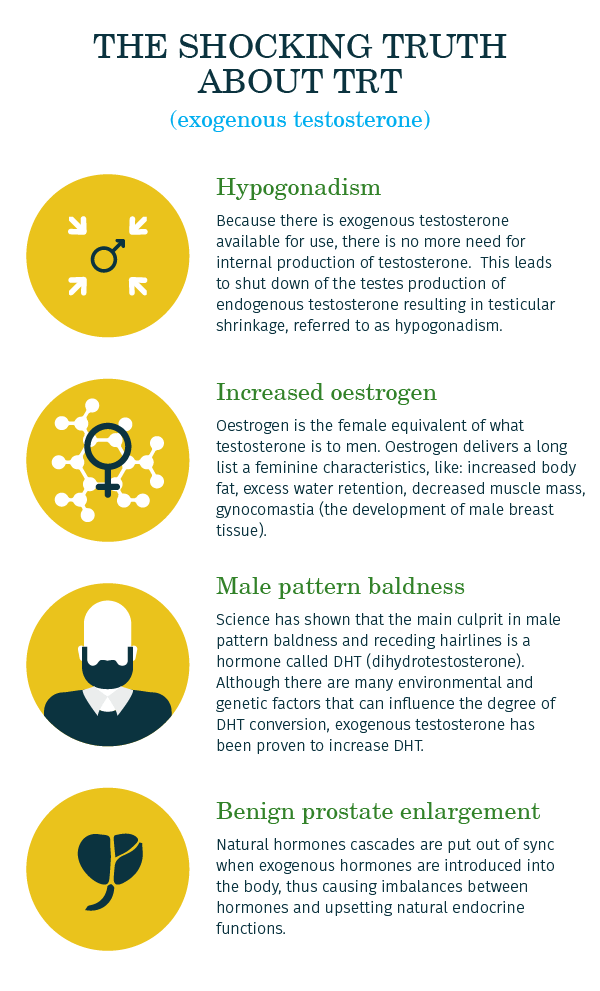
Here I will discuss four of the negative side effects associated with exogenous testosterone use:
- Hypogonadism.
- Increased estrogen.
- Male pattern baldness (Androgenetic Alopecia).
- Benign prostate enlargement (BPH).
Hypogonadism is caused by the use of exogenous testosterone
The use of exogenous (external) testosterone, or any other synthetic androgenous hormones effectively break natural testosterone production and associated regulatory hormonal cycles.
Here's why...
Leutenising hormone is central in regulating the androgen function of the testes, when LH reaches the gonads it stimulates them to produce testosterone. This process also works in the opposite; the release of testosterone suppresses the release of the gonadtrophic hormones; leutenising hormone and follicle stimulating hormone.
This is the basic mechanism of hormone regulation of the HPTA .
Exogenous testosterone causes "negative feedback" between the testes and the hypothalamus. Since testosterone suppresses the release of LH and FSH, the leydig cells in the gonads cease all output of natural testosterone for at least the duration that exogenous testosterone is used.
Furthermore the same is also true for the hypothalamus, production of LH and FSH is also stopped. Essentially each endocrine gland gets disconnected from its partner in the chain resulting in the disunification of the three glands and their particular endocrine function.
The resultant effect on the testes is hypogonadism which significantly decreases natural testosterone output and in some cases testosterone output is completely shut down.
Side effects of low testosterone will not be experienced until enough clearance time has passed since the time of stopping exogenous testosterone treatments. After which, low testosterone due to hypoganadsim, will be experienced.
The effects of low testosterone are in complete polarity from the associated effects of high testosterone:
- Decreased muscle mass.
- Decreased strength.
- Decreased libido.
- Decreased athletic performance.
- Decreased recovery.
Testicular recovery
Although there are certain pharmaceutical treatments available to treat testicular dysfunction and hypogonadism, none of these are proven to be totally effective. Exogenous hormones such as human chorionic gonadotropin (HCG) can be used to aid in reversing hypogonadism.
HCG can temporarily stimulate the production of LH and thus lead to an increase in natural testosterone production by the testes. However, as with exogenous testosterone, once stopped, its actions soon falter.
Because the stimulus of LH production through exogenous HCG is not synchronistic with the internal HPTA mechanisms, and therefore once stopped so do its effects on natural testosterone production.
Thus for the most part only allowing testosterone to be elevated while HCG use is continued.
Science does not yet fully understand these endocrine systems, although the pituitary is thought to be the master control centre, we do not yet know what the root control of all these systems is - leaving for a chicken and egg scenario.
A relatively new branch of science called cybernetics (the study of control and regulatory systems), is being applied to endocrine functions to try and better understand the exact process of how these regulatory bio-feedback mechanisms fundamentally work.
What science does know; exogenous hormone supplementation suppresses the production of the equivalent endogenous hormone.
Exogenous testosterone increases estrogen
Estrogen's are the female equivalent of what androgen's is to men. Estrogen's deliver a long list a feminine characteristics, here are some of them:
- Increased body fat.
- Excess water retention.
- Decreased muscle mass.
- Gynocomastia (the development of male breast tissue).
Mechanism of exogenous testosterone increasing estrogen
Elevated testosterone levels through the use of exogenous testosterone can often lead to an increase in the female hormone estrogen. This happens by way of another regulatory hormonal pathway. When testosterone levels rise too high, creating an imbalance in hormone regulation, an enzyme referred to as aromatase (estrogen synthetase) is released.
Aromatase converts androgen's into estrogen's by way of "aromatisation"; a chemical term for the process of electron redistribution to create a six carbon aromatic ring. Elevated estrogen levels in men is highly undesirable, leading to several unwanted side effects outlined above.
These effects can be counteracted with other drugs such as but not limited to, Arimidex, Letrozole and Aromasin. These drugs are collectively known as Aromatse inhibitors; they work by inhibiting the aromatase enzyme and therefore preventing the biosynthesis of estrogen's from androgen's.
Take heed as these drugs also interfere with internal regulation of natural hormone production, along with having various other side effects.
Estrogen levels can also increase during post cycle exogenous testosterone use. During an "off cycle" period as exogenous testosterone levels decline, the body's production of natural endogenous testosterone is minimal, in fact natural testosterone levels will remain at a minimum until the testes recover from hypogonadism.
For the duration of the "off cycle" period, estrogen levels, due to natural hormone imbalances caused by exogenous testosterone use, typically increase, bringing forth undesirable effects outlined previously.
Increasing testosterone can accelerate male pattern baldness
Science has shown that the main culprit in male pattern baldness and receding hairlines is a hormone called DHT (dihydrotestosterone) (1). DHT is an androgenic hormone that is derived from testosterone via an enzyme called 5-alpha reductase; this enzyme facilitates the conversion of testosterone to DHT.
Although there are many environmental and genetic factors that can influence the degree of DHT conversion, exogenous testosterone has been proven to increase DHT. This is not a good scenario for hair loss when considering that statistics show that by age 35 40% of American men have noticeable hair loss; using a synthetic testosterone will significantly increase male pattern baldness.
DHT increases the risk of Benign Prostate Hyperplasia
DHT has also been linked to BPH (2), which comes with a hoard of negative health effects. An enlarged prostate gland can cause difficulty with urination causing an over frequent need to urinate along with difficulty in successfully emptying the bladder.
Although BPH is typically more predominant in men of the age of fifty or over, younger men using high doses of exogenous testosterones increase their risk of developing BPH due to the increase in DHT.
How to best increase testosterone (do it naturally)
The best scenario for increasing testosterone, is to optimise natural endogenous production through maximising output of testosterone in the testes. Doing so will ensure better health and longevity of endogenous hormone production and endocrine systems in general.
Most men are not fulfilling their maximum testosterone output due to insufficiency in dietary nutrition and/or lifestyle. However, by making a few key changes in these areas, testosterone can be increased to a point of maximum enrichment.
An added benefit of maximising natural testosterone output through diet and supplementation is that this will not negatively affect natural endocrine functions and therefore will not turn off or cause an imbalance between any hormones, whereas the use synthetic hormones do.
Although natural testosterone levels may not peak as high as with exogenous testosterone use, this scenario does have several associated benefits:
- Estrogen levels remain in balance
- Hypogonadism is totally avoided
- Testosterone levels are maximised
- Testosterone levels can be maintained
19 Proven ways to quickly increase testosterone:

- Eat Avocado's to reduce DHT
- Brazil nuts are king for testosterone
- Tomatoes and Watermelon are high in lycopene
- Eat pumpkin seeds
- Pastured eggs contain the building blocks of testosterone
- Increase your beef: eat grass fed beef
- Consume extra zinc
- Supplement with boron
- Reduce cortisol - raise testosterone
- Adaptogenic herbs balance cortisol
- De-stress with hot stone massages
- Meditate and do yoga to reduce anxiety
- listen to music
- Escape the city
- Lifting weights boosts sex hormones
- Take 5-HTP before bed
- Supplement with Theanine prior to sleeping
- Get lean: lower body fat = increased testosterone
- Get 8 hours of sleep every night
Best plan of action to increase testosterone naturally
I would recommend incorporating a bunch of foods into your diet, some of these are natural DHT blockers, and some actually increase testosterone. These foods are all nutrient dense foods which nutrient profiles:
- Avocado
- Brazil nuts
- Tomatoes and Watermelon
- Pumpkin seeds
Avocado
Avocado contains high amounts of a phytosterol (plant based steroid) called beta-sitosterol; this inhibits the 5-alpha reductase enzyme that is responsible for converting testosterone into DHT (3).
Brazil nuts are the kings of nuts for increasing testosterone
Numerous studies have proven that selenium has a dramatic effect on testosterone, furthermore selenium also provides potent antioxidant protection for the prostate gland (4, 5). Sounds good right? The trouble is that most people fall short on their consumption of selenium.
Soils are one of the fundamental bases for life and as such the nutrients contained in them directly affect the nutrient content and quality of the foods that are grown in them.
Due to topsoil depletion from agriculture, particularly chemical-heavy farming techniques and deforestation which increases erosion, fruits and vegetables and other plant based foods are generally lacking in essential nutrients such as selenium.
Nevertheless, brazil nuts still have the highest concentration of selenium of any food on the planet! No joke! These bad boys have around 500% more selenium per serving than the next closest food (yellow fin tuna).
But wait there's more...
Brazil nuts have a fantastic ratio of polyunsaturated to monounsaturated fats and are also a great source of natural cholesterol which can further help to increase testosterone levels.
Pro Tip:
Eat 4-6 organic brazil nuts in their brown skins directly before bed to help increase testosterone levels naturally. Buying organic should ensure soil nutrient quality and therefore ensure nutrient quality of the brazil nuts.
Tomatoes and Watermelon
Tomatoes and Watermelon are both high in the phytonutrient (plant based nutrient) called lycopene. Lycopene is a natural DHT inhibitor and also has great antioxidant protection for the prostate gland.
Tomato puree rather than tomatoes is the best source of lycopene as the puree is far more concentrated and contains higher amounts of lycopene than whole tomatoes.
Pro Tip:
Consuming a teaspoon of organic tomato puree daily will provide you with enough lycopene to maintain optimal antioxidant protection for your prostate gland.
Pumpkin seeds
Pumpkin seeds are also naturally high in beta-sitosterol along with another potent phytosterol, delta-7 sterine. While the evidence on this plant sterol is not yet conclusive studies have shown great promise for delta-7 sterine; it may actually compete with DHT receptors and thus block its effects.
Pro Tip:
Eat 30 grams of organic pumpkin seeds daily, as a snack or as part of a meal to help keep DHT at bay.
Other factors that can increase testosterone levels
Fats - the building blocks of testosterone
For the most part dietary fats get a lot of bad press. However we must distinguish between "good fats" and bad fats". Some fats are actually essential and cannot be manufactured by the body from other dietary sources and therefore ideally need to be consumed on a daily basis.
Good fats have many important functions that play a key role in maintaining optimum health. Here are just a few health benefits from consuming good fats:
- Allow absorption of fat soluble vitamins
- Reduce inflammation
- Improve insulin sensitivity
- Improve hormone production
- Improve brain and cognitive function
Cholesterol and Testosterone
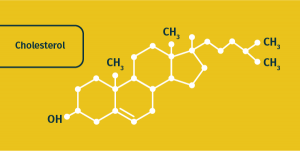
Endogenous testosterone is metabolised from cholesterol and if consumption of dietary fats containing cholesterol is too low testosterone output can be hampered.
Cholesterol, much like testosterone is made from carbon, hydrogen and oxygen; its empirical formula is C27H46O and is a major precursor in the biosynthesis of various steroid hormones, including testosterone (6).
Although consistently high levels of ldl cholesterol can lead to "furring" of the arteries, a condition known as atherosclerosis, which can lead to circulatory problems, strokes and even heart attacks. A healthy cholesterol ratio of good and bad cholesterol (hdl/ldl) can easily be managed and maintained through a healthy diet and lifestyle.
The bottom line
You need cholesterol for optimal testosterone, and if you aren't getting enough, it's likely that your not getting that increase in testosterone you want. The yolk of an egg contains a mixture of proteins, fats, emulsifiers and other nutrients including cholesterol. All eggs contain cholesterol but free range organic eggs have the best cholesterol.
The feed of the chickens that lay the eggs can significantly affect the quality of the nutrients contained within egg itself, therefore eggs that are laid from chickens that are free to roam and are fed on natural organic feed are superior.
An average egg yolk contains approximately one gram of cholesterol.
Pro Tip:
Eat two two whole eggs daily and consume three two hundred and fifty gram portions of organic grass fed beef steaks a week. This will ensure you will have your cholesterol needs covered.
Essential minerals increase testosterone
Minerals play an integral part in increasing testosterone production and because nutrients work in synergy, the absorption of one nutrient may depend on the presence of another cofactor and so on and so forth. Ergo taking a full spectrum of nutrients (minerals and vitamins) is always best practise. However in this instance there are two main mineral players that significantly affect testosterone output.
Zinc
It is of no coincidence that Zinc, for the most part, has become a fundamental ingredient in most testosterone boosting supplements. Simply put Zinc is essential for testosterone production (7). Inside the human body zinc pools are small and easily depleted; zinc is lost in sweat and in male ejaculation.
The absorption of zinc is also affected by minerals such as copper, fibre and other chemical substrates found in mixed meals. Even for those with varied diets, for the above reasons, I suggest supplementing with twenty to twenty five milligrams of zinc per day. Because Zinc is so easily depleted, a lesser dose will not optimally increase testosterone.
Some of the best foods sources are:
- Pastured eggs
- Oysters and other sea foods such as crab, lobster and prawns.
- Red meat
- Cashew nuts
- Spinach
Pro Tip:
Source non-farmed sea foods from pristine waters that are heavy metal and pollutant free.
Boron
Studies have indicated that Boron may be essential for the production of steroid hormones including testosterone (8). However, boron does not increase testosterone as such, rather fall short on this essential mineral and testosterone output will become less than optimal.
The best dietary sources of boron are; nuts, dates and raisins. However, due to farming techniques, pesticides and poor soil quality, present day food is generally low in this mineral.
Here are some of the best whole food sources of boron in their respective orders:
- Raisins
- Almonds
- Apricots
- Avocado
Pro Tip:
Supplement with two milligrams of boron daily, preferably taken before bed.
Decrease cortisol = increase testosterone
Cortisol akin to testosterone is a steroid hormone and forms part of a collection of hormones referred to as glucocorticoids released in the adrenal cortex of the adrenal glands.
Cortisol has an empirical formula of C21H30O5 and is naturally produced under conditions of either low blood glucose or stress; both physical and emotional. Unlike the anabolic actions of testosterone, cortisol is a catabolic hormone; it breaks down larger complex molecules into smaller simpler molecules.
Cortisol stimulates the breakdown of glycogen into glucose, increasing blood glucose levels when needed. Proteolysis; the breakdown of muscle tissue into amino acids is also another action of cortisol. Cortisol levels have an inverse correlation to endogenous testosterone levels; the higher testosterone the lower cortisol and vice versa, ergo cortisol suppresses testosterone (9).
Minimising cortisol production is imperative to maintaining optimum testosterone levels. Here are my top tips for minimising cortisol:
Adaptogenic herbs reduce cortisol
If you haven't yet heard about adaptogenic herbs before then you're missing out!
Adaptogenic herbs are one of nature's little miracles and although these have been used in traditional Chinese medicine for literally thousands of years, western medicine is just catching on.
This is for good reason! Nature has a special way of making molecules and it appears that plants have a harmonious way of doing so, which is far superior to any man-made synthetic versions.
What are Adaptogenc herbs?
In order for a herb to be classed as "adaptogenic", it must, according to world renown master herbalist David Winston, meet 3 specific criteria:
1.) The substance is relatively non-toxic to the recipient.
2.) An adaptogen influences many organs or body systems (non-specific) and acts by increasing resistance of the organism to a broad spectrum of adverse biological, chemical, and physical factors.
3.) These substances help modulate system function and maintain homeostasis
According to Winston there are just 13 true adaptogenic herbs:
American Ginseng root, Ashwagandha root, Asian Ginseng root, Cordyceps, Dang Shen root,, Eleuthero root, Holy Basil herb, Jiaogulan herb , Licorice rhizome, Reishi fungus, Rhaponticum root, Rhodiola root, Wu Wei Zi berries/seeds (Schisandra).
How adaptogenic herbs balance stress-related cortisol
Stress can be both mental and physical, nevertheless both have the same net effect; An increase in stress-hormones such as cortisol. Although cortisol is not an exclusive stress-hormone, for example there are others:
Adaptogenic herbs basically "counter" the effects of stress hormones and have a number of different mechanisms in which they do this. Adaptogens can reduce stress-related enzymes known as c-Jun N-terminal kinases or JNKs for short. In lay terms, these JNKs increase inflammation and oxidative stress that negatively affect cellular energy (ATP) production.
Furthermore one study in particular showed that ashwaganda significantly reduced cortisol content of adrenal glands, and actually lowered cortisol levels.
Although adaptogenic herbs have a "general classification", each has its own unique and subtle effects yet all of them are effective at countering stresses. This is due to the vast array of chemical constituents found in these herbs.
Ashwaganda, for example contains a mixture of alkaloids (isopelletierine, anaferine, cuseohygrine, anahygrine, etc.), steroidal lactones (withanolides, withaferins) and saponins sitoindosides and acylsterylglucosides. Thus is why in ayurveda each herb has its own particular uses.
In terms of reducing cortisol to increase testosterone, ashwaganda (10) has to be the adaptogen of choice. It is traditionally used to treat anxiety, insomnia, nervous exhaustion as well as various other conditions.
Pro Tip:
Try supplementing with KSM-66 aswagandha - a standardised extract with a guaranteed potency of 5% Withanolides.
Other effective ways to de-stress include:
- Regularly take hot stone massages
- Meditate and do Yoga
- Listen to music
- Take a walk in the countryside
LEARN MORE > Yoga & Meditation For Weight Loss 3 Facts You Really Need To Know
Weight lifting is proven to increase testosterone
Numerous studies observed worldwide all share the same consensus; weight lifting, resistance training and super-sets, increases testosterone levels, so much so this has now become a well established scientific fact (11). Exercise induced testosterone is hugely effective and as such I'd suggest three weight training sessions a week.
But what exercises are best to increase testosterone?
Now that's a very good question, if you think you can just go to the gym and do a couple of sets of cable flies and jack your t levels up, your WRONG! Your going to have to lift some WEIGHT, and perform a bunch of free weight basic compound movements. On a weekly basis you will need to do a few good sets of each:
- Squats
- Dead lifts
- Bench press
- Military press
- Barbell rows
- Barbell curls
- Chin ups
- Dips
I'm not suggesting that be your routine, rather I'm suggesting you add some, if not all of these exercises into your weekly training regime. Rep wise, shoot for 6-10 reps on your maximum set, always done to failure and under complete muscular control.
Reducing body fat can increase testosterone
Even if you are following all of my other tips to increase testosterone, you could easily fall short on this one! In order to maintain peak testosterone, it is highly important that you keep a relatively low level of body fat - year round. Now we are not talking 3-5% looking like a mr olympia bodybuilder! Anything between 10-20% should be fine.
But you're probably wondering:
"How does reducing body fat actually increase testosterone?"
So here's the deal, having too much body fat can actually decrease testosterone (12) due to an enzyme called aromatase (estrogen synthase). This is because aromatase is produced inside fat cells. Simply put, the higher your body fat percentage, the more fat cells you have and thus in turn your body is able to produce more of the aromatase enzyme.
As previously explained, aromatase plays a key role in the biosynthesis of estrogens by catalysing steroidogenesis reactions, in particular the aromatisation of estrogen's to androgen's. In lay terms this simply means that it aids in the conversion of testosterone to estrogen. Think of the exact step-by-step process as this:
Increase in body fat -> Increase in aromatase -> Increase in estrogen -> Decrease in testosterone
In fact the New England Research Institutes (NERI) performed of a study of 1,822 men which confirmed that a man's waist size is the single strongest predictor of low testosterone levels.
LEARN MORE > How To Lose Weight Fast: 10 Smart Ways (Guaranteed To Work)
Sleep regulates hormones
A good night's sleep may well leave you refreshed and rejuvenated for the day ahead, but did you know that sleep is also imperative for increasing testosterone output? Various studies all show the same findings; less sleep equals less testosterone (13).
Our circadian rhythms (sleep wake cycles) are governed by the earth's celestial orbit around the sun. Morning sunlight stimulates endocrine functions and hormone release that govern wakefulness. The contrasting stimuli from dark and light regulate different endocrine functions, and thus release different hormones.
At the very top of this hormone cascade is a hormone called melatonin. Testosterone production lies downstream of melatonin; decreased melatonin ultimately leads to decreased testosterone. Poor sleep is proven to lower melatonin. To increase testosterone I suggest a solid eight hours of sleep daily.
Pro Tip:
Take one hundred milligrams of 5-htp (a precursor of melatonin) combined with theanine, an extract of tea.
This combination will assist in melatonin production, help relax the body, and prepare you for a good night's sleep.
Summary
Although a high testosterone level comes with a lot of positives, increasing testosterone through synthetic medicines is only a quick fix and long term will not provide any sustained benefit to your testosterone level or health. Beware of the many bad side effects these drugs can bring.
The best way to increase your testosterone level is to do it naturally, and follow all the methods discussed in this blog. If do you follow these principles and tips, not only will you be able to safely and effectively increase your testosterone, you'll be able to maintain it too!
So now it's your turn, do you have a tip to increase testosterone you'd like to share? Have you tried any of the tips in this guide?
Article by Paul Jenkins CEO and founder of DNA Lean®
Scientific Reference Data:
1. Comparative studies on level of androgens in hair and plasma with premature male-pattern baldness.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/14757277
2. The role of dihydrotestosterone in benign prostatic hyperplasia
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/12657354/
3. A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial to determine the effectiveness of botanically derived inhibitors of 5-alpha-reductase in the treatment of androgenetic alopecia.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12006122
4. Relationship between serum levels of testosterone, zinc and selenium in infertile males attending fertility clinic in Nnewi, south east Nigeria.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23678636
5. Efficacy of Selenium and/or N-Acetyl-Cysteine for Improving Semen Parameters in Infertile Men: A Double-Blind, Placebo Controlled, Randomized Study
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0022534708027018
6. The Role of Lipoproteins in Steroidogenesis and Cholesterol Metabolism in Steroidogenic Glands*
https://academic.oup.com/edrv/article-abstract/3/3/299/2548754/
7. Zinc status and serum testosterone levels of healthy adults.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/8875519
8. Nothing Boring About Boron
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4712861/
9. Cortisol-Induced Suppression of Plasma Testosterone in Normal Adult Males
https://academic.oup.com/jcem/article-abstract/43/3/622/2684748/Cortisol-Induced-Suppression-of-Plasma
10. An Overview on Ashwagandha: A Rasayana (Rejuvenator) of Ayurveda
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3252722/
11. Testosterone physiology in resistance exercise and training: the up-stream regulatory elements.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21058750
12. The hypogonadal-obesity cycle: role of aromatase in modulating the testosterone-estradiol shunt--a major factor in the genesis of morbid obesity.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/10342671
13. The relationship between sleep disorders and testosterone in men
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3955336/
















 USD
USD
 EUR
EUR